Rebate For Solar Power – Solar Power rebates are available in several forms. These include small-scale technology certificates and Federal tax credits. These rebates can help you pay for your solar power system. Find out more about these rebates. Below are some examples of rebates that may be available.
Certificates for small-scale technology
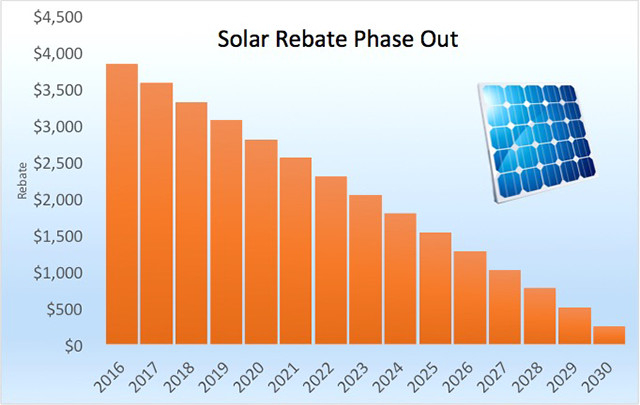
The STC is a certificate that can be used to claim a solar power rebate. The STC is calculated using the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme’s (SRES), which takes into account the date of installation, the location and the amount of electricity the solar PV system can generate over its lifetime. Although STCs can be issued for as long as 20 years, the deeming period decreases each year as the scheme ends.
STCs can be issued for panels with solar photovoltaic power less than 100 kW. They are produced as a result of the SRES, an initiative by the federal government to encourage the use of small-scale renewable energy systems. These solar panels can generate up to a megawatt hour of electricity, and the number of STCs issued will depend on the installation date and location.
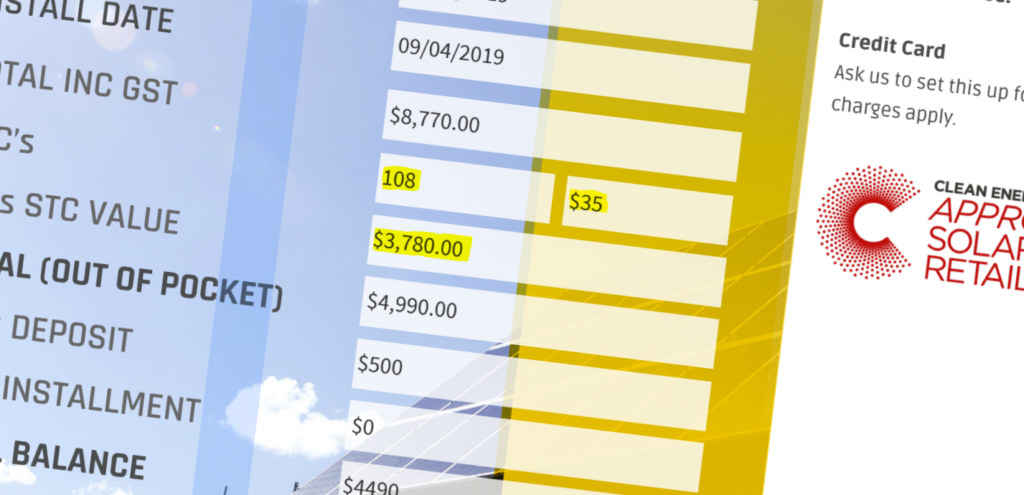
STCs can be purchased, sold, or traded to offset the cost of solar panels and other small-scale technologies. You can get rebates up to $2700 by using small-scale technology certificates in Australia.
Federal tax credit
The Federal tax credit for solar power is an incentive for people who use solar energy to power their home or business. You must own your solar PV system to be eligible for the credit. It cannot be leased or purchased through a solar power purchase agreement. Nevertheless, the credit does cover solar PV cells, panels, wiring, inverters, and other solar system components.
The 2005 Energy Policy Act created the solar investment tax credit. Although originally scheduled to expire in 2007, it was extended several times by Congress due to its popularity with homeowners. The solar tax credit will rise from 26% to 30% starting in August 2022. This credit level will continue until January 1, 2033. After that, the credit will gradually decrease to 22% and eventually phase out entirely in 2035.
The Federal tax credit for solar power is available to those who install a solar photovoltaic system on their primary or secondary residence. However, the system must be financed by the homeowner, and must be located at their primary or secondary residence. You may also be eligible if you participate in a community-based solar project.
State sales tax exemption
New York State Department of Taxation and Finance recently published a publication that explains its exemptions from sales tax for solar energy systems. The publication details how to claim the exemption and details specific rates for solar energy equipment in each jurisdiction. It also provides additional guidance on the process. This publication is an excellent resource for those interested in solar energy for their homes and businesses.
There are 48 different rates for residential solar energy systems and 93 different rates for commercial solar energy systems. Only eight jurisdictions, however, have chosen to exempt commercial systems from the 0% rate. In addition, significantly more local jurisdictions are now taxing electricity generated by commercial solar energy systems.
Solar tax exemptions are another important incentive to consider. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs of solar panels. Although these tax benefits are not available in every state, they can make solar panels more affordable. A state sales tax exemption could reduce the cost of your solar installation to as low as $16,000, making it more affordable.
Net metering
Net metering allows homeowners to get credits from their local utility companies in return for their excess solar electricity. The net metering system has a number of conditions for eligibility. It must belong to the same customer, be on the same property and be in the same load zone. The New York Independent System Operator sets these parameters and reserves the right to investigate individual customer accounts. Net metering accounts must also be separately metered and operated from other solar projects.
Net metering works to reduce the overall cost of electric power, which benefits consumers and the environment. By reducing demand for electricity, the program decreases the need for transmission upgrades and contributes to the reliability of the electric grid. In addition, it creates jobs in the solar supply chain. Today, the solar industry employs 250,000 people in the US and is one of the fastest growing industries in the country. This industry has thrived because of the strong state net-metering policies.